|
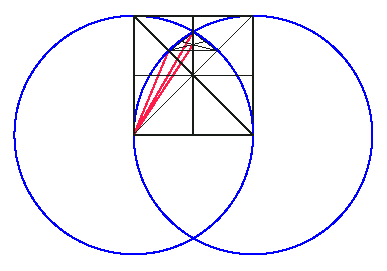
Fig. 9. Simplified illustration of 'harmonic' proportions
A, B and C (drawing: Center for the Study of Architecture):
- C is equal to the radius of the blue circles, the base line
of the square, and the side of the equilateral triangle created
by this case of Euclid 1.1. C is also the apex of a 105°
triangle, whose base is determined by the intersections of the
straight and 'curved' diagonals of the square.
- A is equal to the dimension from the left end of the base
line to the left point of the 105° triangle's base (as if
this were an x/y graph).
- B is equal to the dimension from the left end of the base
line to the centroid of the 105° triangle (alternate construction
method to that seen in Figure 8).
return to text
 |


